Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a condition that affects the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system controls many of the body’s involuntary functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
In people with POTS disease, the autonomic nervous system does not work correctly, which can cause several symptoms, including an abnormally high heart rate when standing up or moving around. POTS disease is a relatively rare condition that can occur in children and adults.
Causes of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome
There are several possible causes of POTS, and the exact cause is unknown in many cases. However, some potential causes include the following:
– Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis can all affect the autonomic nervous system.
– Neurological conditions: Disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Guillain-Barre syndrome can also cause problems with the autonomic nervous system.
– Infections: Viral infections like mononucleosis or Lyme disease can lead to POTS.
– Medications: Some medications (such as beta blockers) can interfere with the autonomic nervous system.
– Pregnancy: Pregnancy can put added stress on the autonomic nervous system.
You must see a doctor for an evaluation if you think you may have POTS. Many of the symptoms of POTS are also seen in other conditions, so getting a proper diagnosis is essential. Treatment for POTS often includes lifestyle changes and medications to help manage symptoms. With proper treatment, most people with POTS can lead relatively normal lives.
POTS Disease Symptoms
There are a variety of symptoms that can occur in people with POTS. Some of the most common POTS disease symptoms include:
– Heart palpitations: These are sudden, often irregular heartbeats that individuals can feel in the chest or neck.
– Lightheadedness: This is a feeling of dizziness or unsteadiness, which can be severe enough to cause fainting.
– Shortness of breath: This may happen when standing up or with activity, and it can be worse if you have a lung condition like asthma.
– Fatigue: People with POTS often feel very tired, even after getting plenty of rest.
– Brain fog: This is a feeling of confusion or forgetfulness, making it difficult to concentrate.
– Headaches: These are often severe and can be made worse by standing up or activity.
– Sweating: People with POTS may sweat excessively, even when they’re not hot or exercising.
– Nausea: This is feeling sick to your stomach, and it can happen with or without vomiting.
– Abdominal pain: This may be cramping or general discomfort in the abdomen.
– Sleep problems: Insomnia is common in people with POTS, and nightmares can also occur.
– Exercise intolerance: People with POTS often cannot tolerate exercise and may feel exhausted after even mild activity.
POTS Disease Treatment
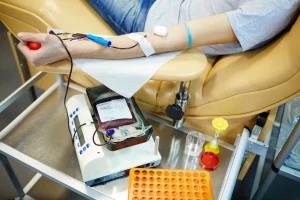
There is no cure for POTS, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. Treatment for POTS often includes lifestyle changes and medications. Additional treatments (such as physical therapy or blood transfusions) may be necessary in some cases. may be necessary in some cases. With proper treatment, most people with POTS can lead relatively normal lives.
Lifestyle Changes
Some lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of POTS. These include:
– Avoiding triggers: If you know what makes your symptoms worse, it’s essential to avoid them. Common triggers include hot weather, stress, and standing for long periods.
– Increasing salt and fluid intake: This can help increase blood volume and reduce symptoms such as fatigue and brain fog.
– Exercising: Although it may be difficult, regular exercise can help improve symptoms. It’s important to start slow and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
– Wearing compression stockings: These can help improve circulation and reduce symptoms such as swelling and pain.
– Managing stress: Stress can worsen POTS symptoms, so it’s essential to find ways to manage it, which may include relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
Medications
There are a variety of medications that medical professionals can use to treat POTS. The type of medication prescribed will often depend on the symptoms being treated. Some common medicines used to treat POTS include:
– Beta-blockers: These can help slow the heart rate and reduce symptoms such as anxiety, palpitations, and dizziness.
– Diuretics: These can help reduce fluid retention and improve symptoms such as swelling and brain fog.
– Salt tablets: These can help increase blood volume and reduce fatigue.
– Ivabradine: This medication can help improve heart function in people with POTS.
– Midodrine: This medication can help increase blood pressure and reduce fainting episodes.
In some cases, doctors may recommend physical therapy to help improve symptoms. Physical therapy can help improve circulation and cardiovascular function. It can also help reduce pain and fatigue. In severe cases of POTS, blood transfusions may be necessary. This treatment can help increase blood volume and reduce symptoms. POTS is a condition that people can manage with lifestyle changes and medications. With proper treatment, most people with POTS can lead relatively normal lives.