Diagnosing and Treating Boils: Bacterial infections or the inflammation of one or more hair follicles can result in the formation of a boil
They are usually painful and can be quite distressing, especially if they are recurring. A boil generally starts off as an inconspicuous pink and tender bump localized to one area which soon develops into a firm, hard inflamed lump that is filled with bacteria-fighting white blood cells and dead skin tissue (pus).
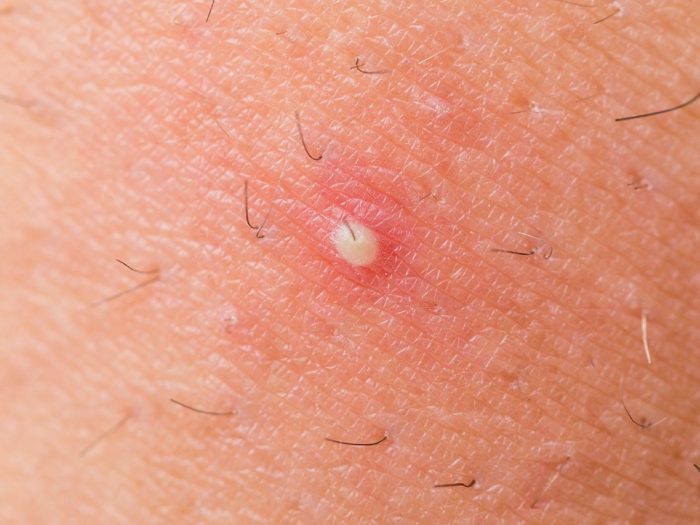
Diagnosing and Treating Boils
The affected area usually gets larger and more painful until the boil bursts and the pus is able to drain. While some Boils disappear within a few days, many can take up to two weeks to heal, which can be very painful and frustrating.
Where do Boils Appear?
Boils can occur anywhere on the skin, although they tend to develop on the face, neck, armpits, buttocks, or thighs.
They also occur most frequently in areas containing hair and/or sweat glands or in areas where chaffing or recurrent friction occurs. In some cases, Boils can occur in interconnected clusters which are then called carbuncles, and in severe cases, they can develop into abscesses.
While anyone can develop Boils and carbuncles, people who have diabetes, a suppressed immune system, poor hygiene, acne, or other skin problems are at a higher risk.
Diagnosing Boils
Most Boils can be adequately treated at home and usually run their course and heal without medical attention. However, in some cases, you may need to visit a general health practitioner to avoid complications. Your doctor will simply examine the affected area to confirm the diagnosis and generally, no other diagnostic tests are necessary.
Tests to Diagnose Boils
- Fever.
- The boil occurs between the buttocks (known as a pilonidal cyst.)
- The boil is very painful and not improving.
- The boil worsens rapidly.
- You have frequent boils.
- There are red lines radiating from the boil which suggests that the infection may have entered the bloodstream.
- You have an underlying condition resulting in immune deficiency.
What Causes Boils?
Boils are generally caused by an infection of a hair follicle. This can occur for a number of different reasons.
Contributing Causes of Boils
- An ingrown hair.
- A splinter or other piece of foreign material that has penetrated the skin.
- Blocked sweat glands that become infected.
- Chaffing clothes.
- Poor hygiene.
- A lowered immune system.
- Diabetes.
- Malnutrition (Vitamin A or E deficiency in particular.)
Help for Boils
There are a number of treatment and prevention options for boils ranging from old home remedies passed down over the generations, to medical interventions and surgery.
The one important thing to remember is that Boils are most commonly related to low immune system functioning. By boosting the immune system, you’ll be able to prevent boils and recurrent infections.
Treatment for Boils
Home Treatment
Boils generally heal by themselves within 4 to 10 days and self-care is usually the only treatment needed. Healing can be speeded by applying a warm cloth to the area or soaking the boil in warm water. This should help to relieve some of the pain and encourage the pus to surface. Once the boil has drained, the area should be washed with antibacterial soap and kept bandaged and sterile as the open wound may be susceptible to further infection.
Special care should also be taken to prevent the spreading of the bacteria which can be transmitted to other areas of the skin or to other people through the pus. You should not squeeze or attempt to pop a boil if it is hard and firm as Boils should only be drained once they have become soft or once a head has formed. It is recommended to leave the boil to burst on its own to reduce the spread of infection to other areas.
Medical Treatment
If the boil requires some medical intervention, your doctor may drain it by making a small incision on the tip of the boil. This will help speed up the recovery, reduce pressure and pain, and it helps to lessen scarring. If the infection is especially deep, a small amount of gauze can be placed over the boil so that it can continue to drain. In addition, a course of oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to help rid you of severe or recurrent infections.
If Boils are a recurrent problem your doctor may also suggest vitamin supplements (especially vitamin A and E) and tests may be done to determine if you have an underlying condition that may be compromising your immune system.
Surgery
Surgery is one of the last measures taken to prevent recurrent Boils. This may include the surgical removal of the sweat glands in the area of the skin that is frequently infected. Surgery is also sometimes necessary when trying to treat pilonidal cysts.
Natural Herbal and Homeopathic Remedies for Boils
There are a number of herbal and homeopathic remedies that can be of great benefit for someone suffering from Boils. Since immune deficiency is one of the highlighted causes of this skin infection, naturally boosting the immune system is the first course of action for many people!
Herbs such as Echinacea Purpurea, Astragalus Membranaceous, Inula Helenium, and Withania Somnifera are well documented for their antiviral, antifungal, and antibacterial properties and their ability to strengthen and assist the immune system. These herbs not only help to treat current infections but work well as a preventative measure so that the Boils do not re-occur.
In addition, there are also homeopathic and herbal ingredients specific to skin ailments that can help speed recovery and keep the affected area clean and clear from harmful bacteria. Silicea, a homeopathic tissue salt, is very effective in helping the body to expel all foreign or toxic matter, including pus, and is frequently recommended in homeopathic dosage to quickly alleviate Boils.
In addition, naturopaths often recommend liver and systemic cleansing herbs such as Silybum Marianus and Gallium Aperine for the treatment of recurring boils.
Self-Care Prevention Measures
There are a number of simple ways to prevent boils from re-occurring:
- Practice good hygiene and wash skin with soap regularly.
- Avoid very tight or chaffing clothing that irritates the skin.
- Clean cuts and scrapes thoroughly.
- Keep the immune system functioning well with a healthy diet and sufficient exercise.
Related Natural Product
Boil-Rx is a safe, non-addictive, FDA-registered natural remedy containing 100% homeopathic ingredients selected to relieve the swelling, pain, and pustules associated with boils. Boil-Rx may be taken as the first sign of skin redness and localized tenderness, as it works quickly to reduce inflammation and discomfort, as well as assist the expulsion of toxins and pus.
This remedy contains a selection of homeopathic ingredients known to support overall skin health, without side effects. Boil-Rx is taken internally and presented in a convenient, concentrated tincture formula. It is easy to ingest and hassle-free with no artificial colors or preservatives. It is safe for all ages, including pregnant women or those who may be breastfeeding.



