The ketogenic diet was designed in 1924 by Dr. Russell Wilder at the Mayo Clinic
It originally was created to treat epilepsy patients. It has recently become very popular for weight loss, due to the results it gives. It has been proven by researchers it can help cancer, Alzheimer’s, and type II diabetes patients.
What does Ketogenic mean?
Ketogenic stems from the word Ketosis, a metabolic process that occurs when the body does not have enough glucose to use as energy. When the body has no access to food, the body will burn fat and create molecules called ketones.
When the body has no access to food, the body will burn fat and create these ketones.
Ketones are produced in the liver, from fat. They are then used as fuel throughout the body, including the brain.
On a ketogenic diet, the entire body switches its fuel supply to run almost entirely on fat. Insulin levels become very low and fat burning increases dramatically.
What does the ketogenic diet consist of?
The Ketogenic diet forces the body to enter the Ketosis state, in order to achieve this, one needs a high-calorie intake, while reducing the number of carbohydrates consumed every day.
Who or how can the ketogenic diet help?
Type II Diabetes
The Ketogenic diet converts fat, instead of sugar into energy. The ketogenic diet may improve blood glucose (sugar) levels while also reducing the need for insulin.
A study published in the journal Nutrition and Metabolism in 2005 evaluated a ketogenic diet in 21 people with type 2 diabetes over 16 weeks. They improved their blood sugar control by 16 percent, on average, and had a weight loss of more than 6 percent, and 17 of the participants were able to discontinue or reduce their diabetes medications.
Cancer
Controlling blood-glucose leptin and insulin levels through diet, exercise and emotional stress relief can be one of the most crucial components of a cancer recovery program. These factors are also crucial in order to prevent cancer in the first place. In 1931, the Nobel Prize was awarded to German researcher Dr. Otto Warburg, who discovered that cancer cells have a fundamentally different energy metabolism compared to healthy cells and that malignant tumors tend to feed on sugar.
More recently, researchers discovered that while cancer cells feed on both glucose and fructose, pancreatic tumor cells use fructose specifically to divide and proliferate.
A ketogenic diet will also elevate ketone bodies, as fat is metabolized to ketones that your body can burn in the absence of food. When combined with calorie restriction, the end result will put your body in a metabolic state that is inhospitable to cancer cells.
Alzheimer’s disease
Several studies have demonstrated that the “neurofibrillary tangles” of proteins found in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients are in part caused by the development of insulin resistance in brain cells.
Neurons depend heavily on glucose as an energy source, especially when the diet is high in carbohydrates. A high carb diet generates high levels of blood sugar (glucose) and insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that pushes glucose into neurons. The problem is that after years of being subjected to high blood sugar and insulin levels, body cells become resistant to insulin’s message.
The cells shut the door on insulin’s request to send in glucose.
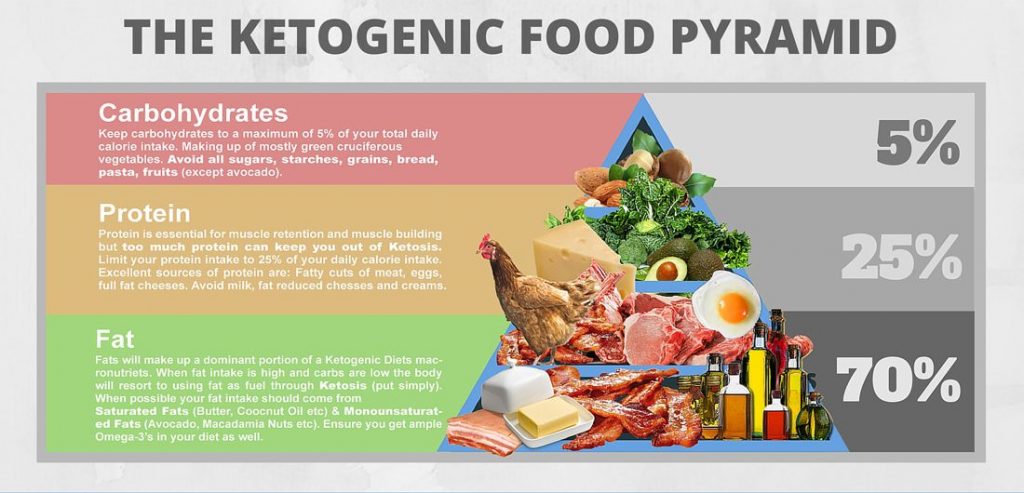
What are the basics of a Ketogenic diet plan?
You should eat foods which are mostly low in carbohydrates and high in fat
Foods you should eat:
- Meat: Red meat, steak, ham, sausage, bacon, chicken, and turkey.
- Fatty fish: Such as salmon, trout, tuna, and mackerel.
- Eggs: Look for pastured or omega-3 whole eggs.
- Butter and cream: Look for grass-fed when possible.
- Cheese: Unprocessed cheese (cheddar, goat, cream, blue, or mozzarella).
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, etc.
- Healthy oils: Primarily extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil.
- Avocados: Whole avocados or freshly made guacamole.
- Low-carb veggies: Most green veggies, tomatoes, onions, peppers, etc.
- Condiments: You can use salt, pepper, and various healthy herbs and spices.
Foods to avoid:
- Sugary foods: Soda, fruit juice, smoothies, cake, ice cream, candy, etc.
- Grains or starches: Wheat-based products, rice, pasta, cereal, etc.
- Fruit: All fruit, except small portions of berries like strawberries.
- Beans or legumes: Peas, kidney beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc.
- Root vegetables and tubers: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, parsnips, etc.
- Low-fat or diet products: These are highly processed and often high in carbs.
- Some condiments or sauces: These often contain sugar and unhealthy fat.
- Unhealthy fat: Limit your intake of processed vegetable oils, mayonnaise, etc.
- Alcohol: Due to its carb content, many alcoholic beverages can throw you out of ketosis.



